Diferencia entre revisiones de «ManuelRomero/grafica/presentacion»
De WikiEducator
(→TRANSFORMACIÓN EN EL PIPELINE GRÁFICO) |
|||
| Línea 110: | Línea 110: | ||
} | } | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | [[Imagen:CoordenadasOpenGL.png]] | + | *Así quedaría |
| + | [[Imagen:CoordenadasOpenGLBásico.png|200px]] | ||
| + | *Lo giramos para ver la coordenada z | ||
| + | [[Imagen:CoordenadasOpenGL.png|200px]] | ||
Revisión de 23:04 11 jun 2013
Esqueleto de un programa openGL
#include <GL/glut.h> // Drawing routine. void escena(void) { glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Clear the buffers including // the depth buffer. glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT, GL_FILL); glBegin(GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP); glEnd(); // Write labels. glFlush(); } // Initialization routine. void setup(void) { glClearColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0); } // OpenGL window reshape routine. void redibuja(int w, int h) { glViewport(0, 0, (GLsizei)w, (GLsizei)h); glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); glOrtho(0.0, 100.0, 0.0, 100.0, -1.0, 1.0); glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); glLoadIdentity(); } // Keyboard input processing routine. void teclado(unsigned char key, int x, int y) { switch(key) { case ' ': case 27: default: break; } } // Routine to output interaction instructions to the C++ window. void printInteraction(void) { cout << "Interaction:" << endl; cout << "Press the space bar to toggle between wirefrime and filled for the lower annulus." << endl; } // Main routine. int main(int argc, char **argv) { printInteraction(); glutInit(&argc, argv); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DEPTH); // Initialize the buffers // including the depth buffer. glutInitWindowSize(500, 500); glutInitWindowPosition(100, 100); glutCreateWindow("circularAnnuluses.cpp"); setup(); glutDisplayFunc(escena); glutReshapeFunc(redibuja); glutKeyboardFunc(teclado); glutMainLoop(); return 0; }
TRANSFORMACIÓN EN EL PIPELINE GRÁFICO
- Coordenadas del objeto (x,y,z,w)
Transformación ModelView
- Coordenadas del ojo
Proyección
- Cooredenadas de recorte
Perspectiva
- Coordenadas del dispositivo
Viewport
- Coordenadas de la ventana (x,y)
===Coordenadas del objeto
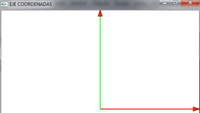
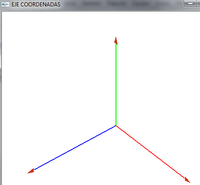
- Dibujamos un eje de coordenadas x,y,z
void dibujaCoordenadas(void){ porFlechitas(); glLineWidth(2); glBegin(GL_LINES); glLineWidth(3); glColor3f(1,0,0);//Eje X glVertex3f(0,0,0); glVertex3f(15,0,0); glColor3f(0,1,0);//Eje X glVertex3f(0,0,0); glVertex3f(0,15,0); glColor3f(0,0,1);//Eje z glVertex3f(0,0,0); glVertex3f(0,0,15); glLineWidth(1); glEnd(); glPushMatrix(); glFlush(); }
- Así quedaría
- Lo giramos para ver la coordenada z