|
|
| Línea 1: |
Línea 1: |
| | {{:Usuario:ManuelRomero/grafica/nav}} | | {{:Usuario:ManuelRomero/grafica/nav}} |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| − | ===Esqueleto de un programa openGL===
| |
| − | <source lang=cpp>
| |
| − | #include <GL/glut.h>
| |
| − | // Drawing routine.
| |
| − | void escena(void)
| |
| − | {
| |
| − |
| |
| − | glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Clear the buffers including
| |
| − | // the depth buffer.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT, GL_FILL);
| |
| − | glBegin(GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP);
| |
| | | | |
| − | glEnd();
| + | {{#widget:Slides}} |
| − |
| + | |
| − | // Write labels.
| + | <div class="slides layout-regular template-default"> |
| − | glFlush();
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | // Initialization routine.
| + | |
| − | void setup(void)
| + | |
| − | { | + | |
| − | glClearColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | // OpenGL window reshape routine.
| + | |
| − | void redibuja(int w, int h)
| + | |
| − | { | + | |
| − | glViewport(0, 0, (GLsizei)w, (GLsizei)h);
| + | |
| − | glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
| + | |
| − | glLoadIdentity();
| + | |
| − | glOrtho(0.0, 100.0, 0.0, 100.0, -1.0, 1.0);
| + | |
| − | glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
| + | |
| − | glLoadIdentity();
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | // Keyboard input processing routine.
| + | |
| − | void teclado(unsigned char key, int x, int y)
| + | |
| − | {
| + | |
| − | switch(key)
| + | |
| − | {
| + | |
| − | case ' ':
| + | |
| − | case 27:
| + | |
| − | default:
| + | |
| − | break;
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | } | + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | // Routine to output interaction instructions to the C++ window.
| + | |
| − | void printInteraction(void)
| + | |
| − | {
| + | |
| − | cout << "Interaction:" << endl;
| + | |
| − | cout << "Press the space bar to toggle between wirefrime and filled for the lower annulus." << endl;
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | // Main routine.
| + | |
| − | int main(int argc, char **argv)
| + | |
| − | {
| + | |
| − | printInteraction();
| + | |
| − | glutInit(&argc, argv);
| + | |
| − | glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DEPTH); // Initialize the buffers
| + | |
| − | // including the depth buffer.
| + | |
| − | glutInitWindowSize(500, 500);
| + | |
| − | glutInitWindowPosition(100, 100);
| + | |
| − | glutCreateWindow("circularAnnuluses.cpp");
| + | |
| − | setup();
| + | |
| − | glutDisplayFunc(escena);
| + | |
| − | glutReshapeFunc(redibuja);
| + | |
| − | glutKeyboardFunc(teclado);
| + | |
| − | glutMainLoop();
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | return 0;
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | </source>
| + | |
| | | | |
| | + | <div class="slide"> |
| | ===TRANSFORMACIÓN EN EL PIPELINE GRÁFICO=== | | ===TRANSFORMACIÓN EN EL PIPELINE GRÁFICO=== |
| − | #Coordenadas del objeto (x,y,z,w)
| + | *Basado en un sistema de visualizacion |
| | + | Objeto 3d ====>>> represntación en pantalla bidimensional |
| | + | 1.- '''''Coordenadas del objeto''''' (x,y,z,w) |
| | Transformación ModelView | | Transformación ModelView |
| − | #Coordenadas del ojo
| + | 2.-'''''Coordenadas del ojo''''' |
| | Proyección | | Proyección |
| − | #Cooredenadas de recorte
| + | 3.- '''''Cooredenadas de recorte''''' |
| | Perspectiva | | Perspectiva |
| − | #Coordenadas del dispositivo
| + | 4.-'''''Coordenadas del dispositivo''''' |
| | Viewport | | Viewport |
| − | #Coordenadas de la ventana (x,y)
| + | 5.-'''''Coordenadas de la ventana (x,y)''''' |
| | + | </div> |
| | ===Coordenadas globales - cooredenadas locales=== | | ===Coordenadas globales - cooredenadas locales=== |
| | *Dibujamos un eje de coordenadas x,y,z | | *Dibujamos un eje de coordenadas x,y,z |
| Línea 166: |
Línea 100: |
| | http://asanchez.cs.buap.mx/arreglos_vertices.pdf | | http://asanchez.cs.buap.mx/arreglos_vertices.pdf |
| | }} | | }} |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | ===Esqueleto de un programa openGL=== |
| | + | <source lang=cpp> |
| | + | #include <GL/glut.h> |
| | + | // Drawing routine. |
| | + | void escena(void) |
| | + | { |
| | + | |
| | + | glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Clear the buffers including |
| | + | // the depth buffer. |
| | + | |
| | + | glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT, GL_FILL); |
| | + | glBegin(GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP); |
| | + | |
| | + | glEnd(); |
| | + | |
| | + | // Write labels. |
| | + | glFlush(); |
| | + | } |
| | + | |
| | + | // Initialization routine. |
| | + | void setup(void) |
| | + | { |
| | + | glClearColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0); |
| | + | } |
| | + | |
| | + | // OpenGL window reshape routine. |
| | + | void redibuja(int w, int h) |
| | + | { |
| | + | glViewport(0, 0, (GLsizei)w, (GLsizei)h); |
| | + | glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); |
| | + | glLoadIdentity(); |
| | + | glOrtho(0.0, 100.0, 0.0, 100.0, -1.0, 1.0); |
| | + | glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); |
| | + | glLoadIdentity(); |
| | + | } |
| | + | |
| | + | // Keyboard input processing routine. |
| | + | void teclado(unsigned char key, int x, int y) |
| | + | { |
| | + | switch(key) |
| | + | { |
| | + | case ' ': |
| | + | case 27: |
| | + | default: |
| | + | break; |
| | + | } |
| | + | } |
| | + | |
| | + | // Routine to output interaction instructions to the C++ window. |
| | + | void printInteraction(void) |
| | + | { |
| | + | cout << "Interaction:" << endl; |
| | + | cout << "Press the space bar to toggle between wirefrime and filled for the lower annulus." << endl; |
| | + | } |
| | + | |
| | + | // Main routine. |
| | + | int main(int argc, char **argv) |
| | + | { |
| | + | printInteraction(); |
| | + | glutInit(&argc, argv); |
| | + | glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DEPTH); // Initialize the buffers |
| | + | // including the depth buffer. |
| | + | glutInitWindowSize(500, 500); |
| | + | glutInitWindowPosition(100, 100); |
| | + | glutCreateWindow("circularAnnuluses.cpp"); |
| | + | setup(); |
| | + | glutDisplayFunc(escena); |
| | + | glutReshapeFunc(redibuja); |
| | + | glutKeyboardFunc(teclado); |
| | + | glutMainLoop(); |
| | + | |
| | + | return 0; |
| | + | } |
| | + | </source> |
TRANSFORMACIÓN EN EL PIPELINE GRÁFICO
- Basado en un sistema de visualizacion
Objeto 3d ====>>> represntación en pantalla bidimensional
1.- Coordenadas del objeto (x,y,z,w)
Transformación ModelView
2.-Coordenadas del ojo
Proyección
3.- Cooredenadas de recorte
Perspectiva
4.-Coordenadas del dispositivo
Viewport
5.-Coordenadas de la ventana (x,y)
Coordenadas globales - cooredenadas locales
- Dibujamos un eje de coordenadas x,y,z
void dibujaCoordenadas(void){
porFlechitas();
glLineWidth(2);
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glLineWidth(3);
glColor3f(1,0,0);//Eje X
glVertex3f(0,0,0);
glVertex3f(15,0,0);
glColor3f(0,1,0);//Eje X
glVertex3f(0,0,0);
glVertex3f(0,15,0);
glColor3f(0,0,1);//Eje z
glVertex3f(0,0,0);
glVertex3f(0,0,15);
glLineWidth(1);
glEnd();
glPushMatrix();
glFlush();
}
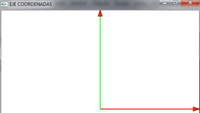
- A OpenGL le especificamos bien por puntos o por vectores estos valores
- OpenGL rederiza en la pantalla y visuzliza dichos puntos según le especifiquemos
- Así quedaría
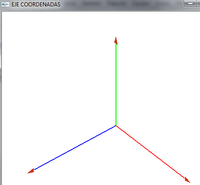
- Lo giramos para ver la coordenada z. Esta parte luego la veremos
- PAra conseguirlo he girado 40º en el eje de x y 40º en el eje de y
.. .. ..
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
glRotatef(40.0f,1,0,0);
glRotatef(40.0f,0,1,0);
glutPostRedisplay();
.. .. ..
- Este eje de coordenadas que hemos dibujado representaría el eje de coordenadas del objeto
- Ahora dibujamos un objeto en él, por ejemplo una tetera
- con la barra espaciadora podemos cambiar su representación, sólida o de alambres
- Representación sólida
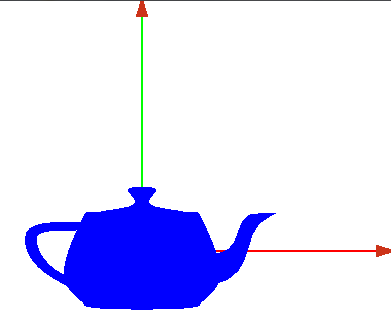
- Represetnación en alambres
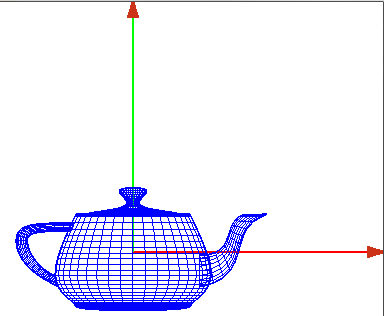
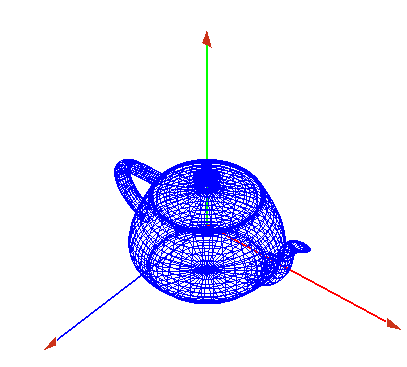
- Ahora hemos dibujado la tetera respecto al eje de coordenadas del mundo
Eje de coordenadas del objeto
- Planteamos un nuevo eje de coordenadas
- Podemos ver que respecto al eje de coordenadas del mundo (0,0,0), tiene los siguientes vectores
(10,10,10)- (15,15,10)
(10,10,10)- (5,15,10)
(10,10,10)- (10,10,15)
- Gráficamente lo podemos ver en la imagen (siempre respecto al eje de coordenadas de nuestro mundo (0,0,0) como centro
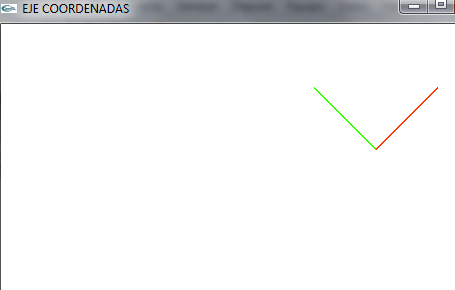
- Lo giramos para ver el componente z (Se observa en diferente posición pues lo he rotado respecto a X e Y de las coordenadas del mundo no de ella misma
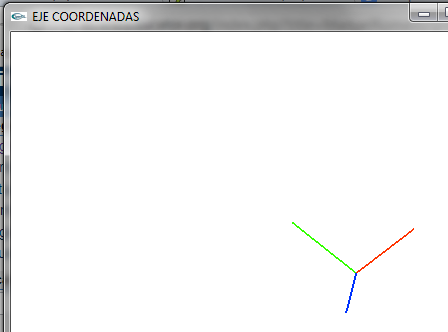
- Vemos los dos ejes de coordenadas
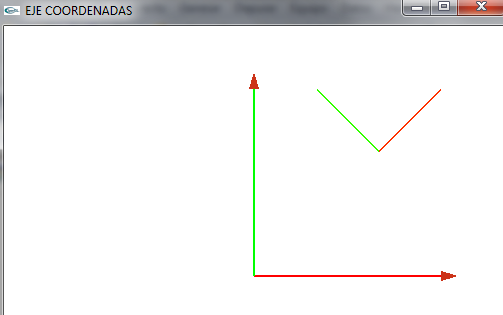
- Lo giramos para verlo un poco mejor
- Vemos el objeto en el eje de coordenadas del mundo global y lo queremos pasar al eje de coordenadas del mundo local o del objeto
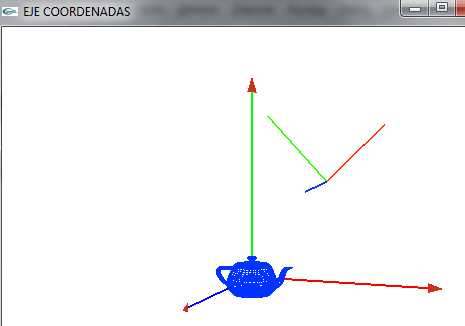 ===Vamos a ver como pasar el objeto a las coordenadas locales
===Vamos a ver como pasar el objeto a las coordenadas locales
- Para ello vamos a multiplicar cada vétice del objeto por una matriz de escena
- Esta matriz permite realizar operaciones de rotación traslación y escalado
- En nuestro caso queremos coger la tetera y
- Trasladarla al punto 10,10,10.
- trasladar 10 unidades en X
- trasladar 10 unidades en Y
- trasladar 10 unidades en Z
- Rotar 15 grados
Son en total 4 operaciones
Esqueleto de un programa openGL
#include <GL/glut.h>
// Drawing routine.
void escena(void)
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Clear the buffers including
// the depth buffer.
glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT, GL_FILL);
glBegin(GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP);
glEnd();
// Write labels.
glFlush();
}
// Initialization routine.
void setup(void)
{
glClearColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0);
}
// OpenGL window reshape routine.
void redibuja(int w, int h)
{
glViewport(0, 0, (GLsizei)w, (GLsizei)h);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
glOrtho(0.0, 100.0, 0.0, 100.0, -1.0, 1.0);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
}
// Keyboard input processing routine.
void teclado(unsigned char key, int x, int y)
{
switch(key)
{
case ' ':
case 27:
default:
break;
}
}
// Routine to output interaction instructions to the C++ window.
void printInteraction(void)
{
cout << "Interaction:" << endl;
cout << "Press the space bar to toggle between wirefrime and filled for the lower annulus." << endl;
}
// Main routine.
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
printInteraction();
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DEPTH); // Initialize the buffers
// including the depth buffer.
glutInitWindowSize(500, 500);
glutInitWindowPosition(100, 100);
glutCreateWindow("circularAnnuluses.cpp");
setup();
glutDisplayFunc(escena);
glutReshapeFunc(redibuja);
glutKeyboardFunc(teclado);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}